Security Group
Overview
Security Groups act as virtual firewalls that control inbound and outbound traffic for Cloud Instances. They provide essential network-layer protection against unauthorized access.
Key Benefits:
- Multi-layer protection alongside other security solutions
- Flexible rule customization per application requirements
- Centralized security policy management
- Instant rule application without server restart
Managing Security Groups
View and manage firewall configurations for Instances and Load Balancers in the Security Group interface.
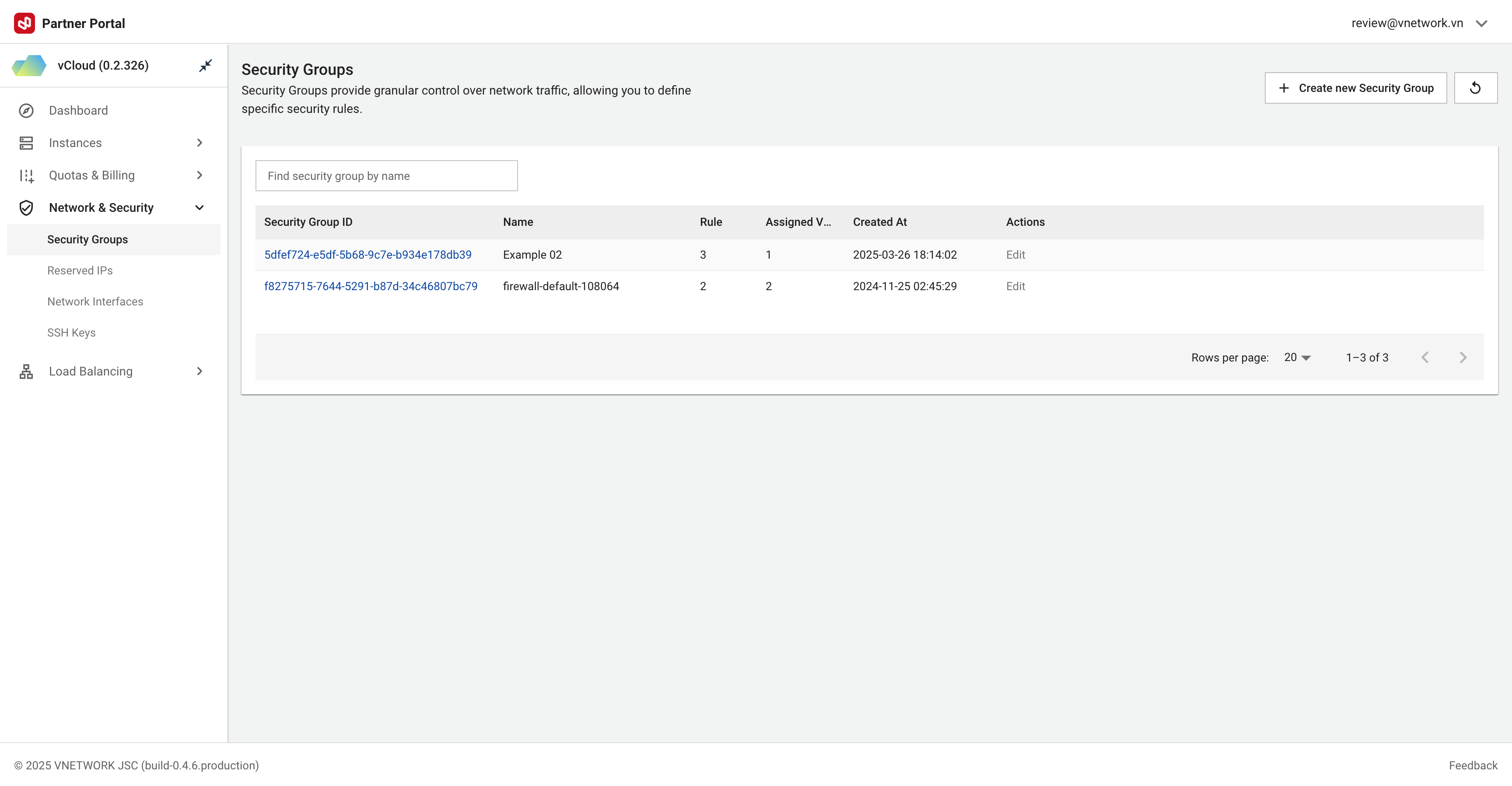 Figure needed: Security Group management interface showing the list of security groups with their IDs, names, rule counts, assigned VMs, and action buttons
Figure needed: Security Group management interface showing the list of security groups with their IDs, names, rule counts, assigned VMs, and action buttons
Interface Components:
- Security Group ID: Unique identifier
- Name: Display name
- Rules: Number of active rules
- Assigned VMs: Number of VMs using this group
- Created At: Creation timestamp
- Actions: Edit/Delete options
Use "Find security group by name" to search for specific groups.
Creating Security Groups
- Click + Create new Security Group
- Enter meaningful name (e.g., web-servers, db-servers)
- Add optional description
- Configure security rules
- Click Create
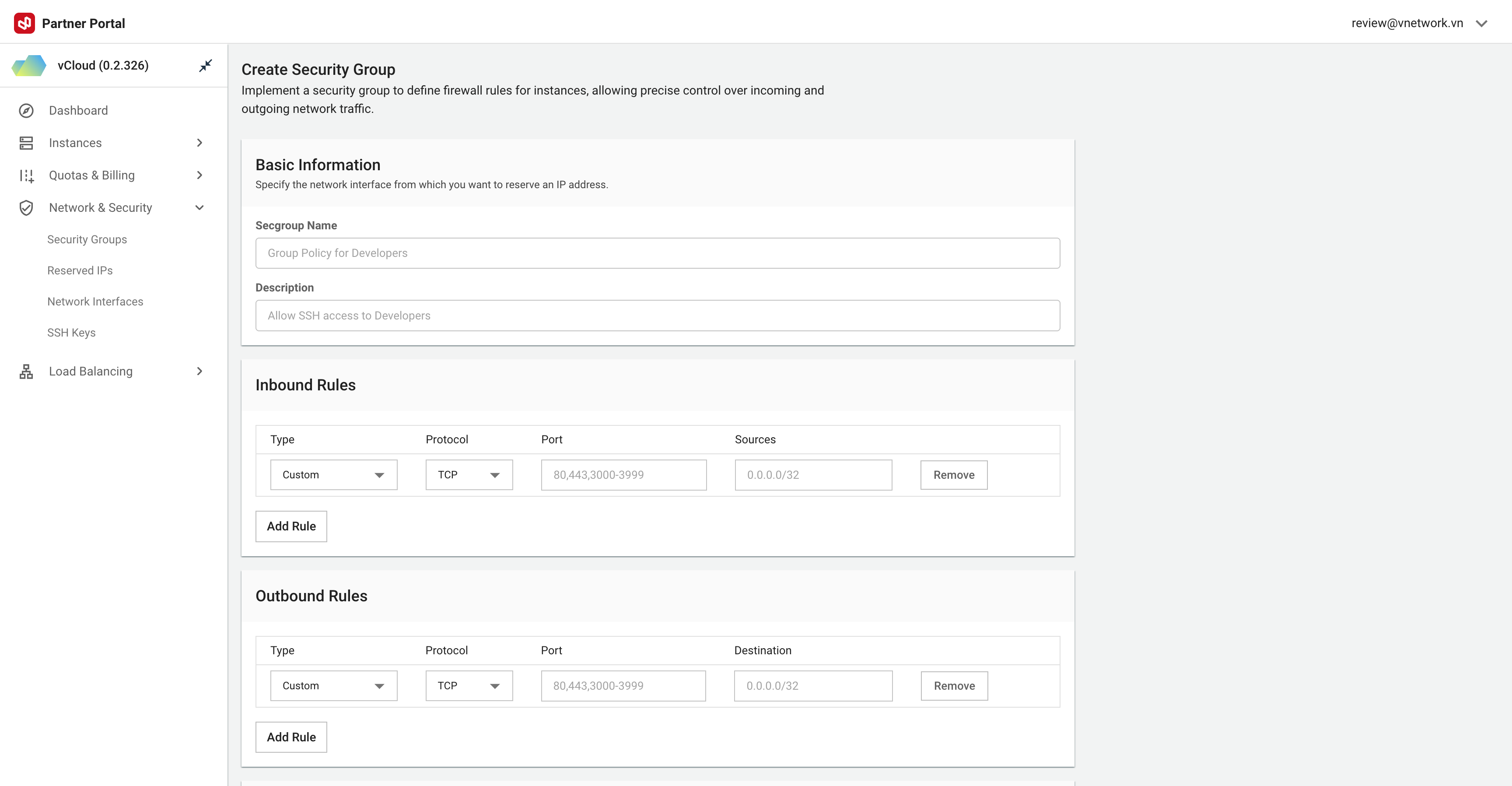 Figure needed: Security Group creation dialog with name field, description field, and rule configuration options
Figure needed: Security Group creation dialog with name field, description field, and rule configuration options
Create separate Security Groups for each system tier (Web, Application, Database) for better management and enhanced security.
Security Rules
Rules define which traffic is allowed or blocked.
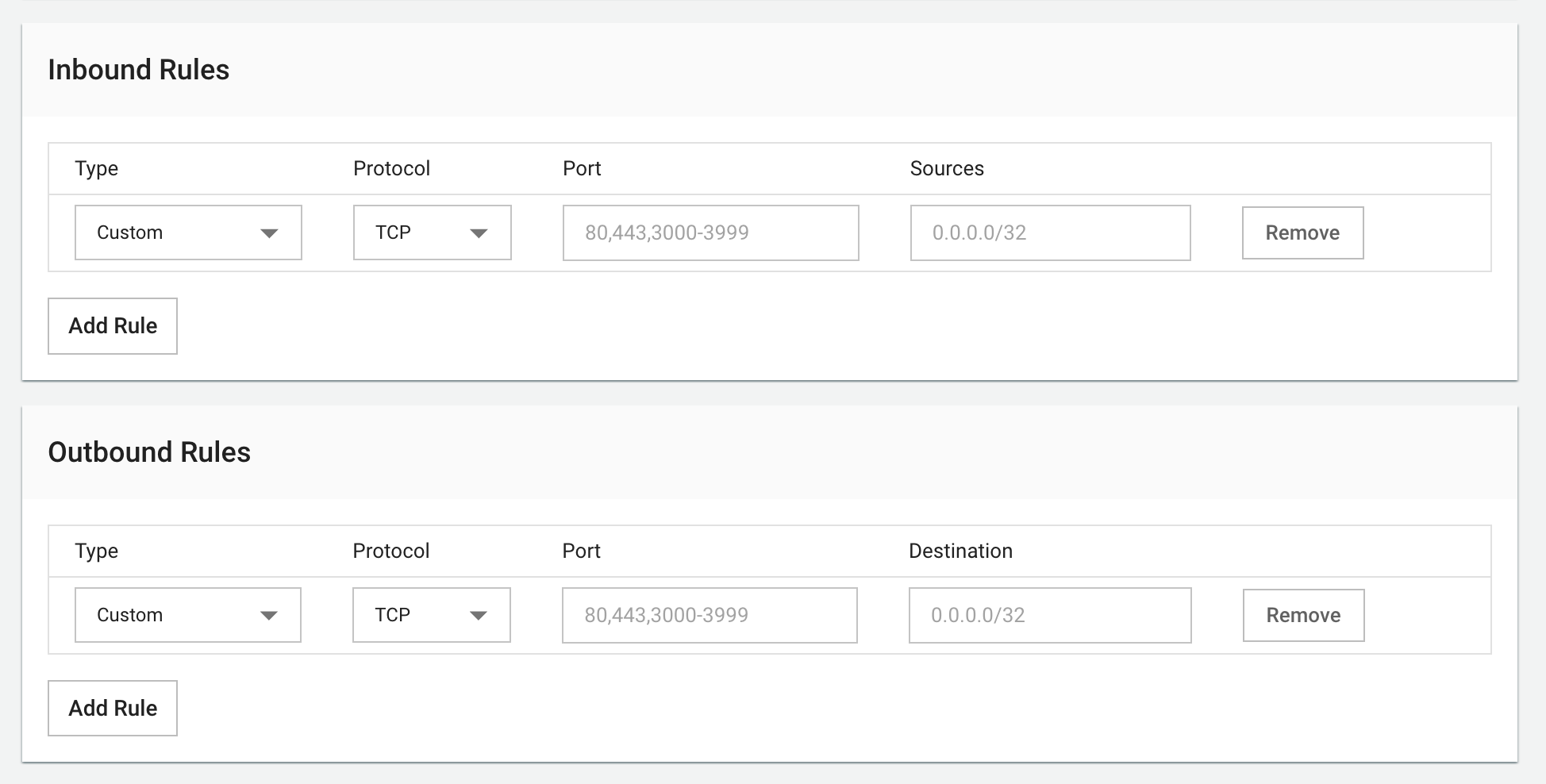 Figure needed: Security Group rules management interface showing a table of rules with direction, protocol, port, CIDR, and description columns
Figure needed: Security Group rules management interface showing a table of rules with direction, protocol, port, CIDR, and description columns
Rule Components:
- Direction:
- Ingress: Inbound traffic (external → server)
- Egress: Outbound traffic (server → external)
- CIDR: IP addresses/ranges
- Specific IP:
192.168.1.10/32 - IP range:
10.0.0.0/24 - All IPs:
0.0.0.0/0
- Specific IP:
- Protocol: TCP (HTTP, HTTPS, SSH), UDP (DNS, NTP), ICMP (ping)
- Port: Single (
80), range (1024-2048), or all (1-65535) - Description: Rule purpose (e.g., "Allow HTTP traffic")
Common Rule Examples:
| Purpose | Direction | Protocol | Port | CIDR | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Web Server | Ingress | TCP | 80, 443 | 0.0.0.0/0 | Allow HTTP/HTTPS from internet |
| SSH Access | Ingress | TCP | 22 | x.x.x.x/32 | Allow SSH from specific IP |
| Database | Ingress | TCP | 3306 | 10.0.0.0/24 | Allow MySQL from internal network |
| DNS | Egress | UDP | 53 | 0.0.0.0/0 | Allow DNS queries outbound |
| ICMP | Ingress | ICMP | - | 0.0.0.0/0 | Allow ping for connectivity tests |
Configuring Rules
Connection Types (with default ports):
- SSH: Port 22
- RDP: Port 3389
- HTTP: Port 80
- HTTPS: Port 443
- ICMP: Ping protocol
- DNS: Port 53
- Custom: Define custom ports
Protocols:
- TCP: Reliable transmission (HTTP, SSH)
- UDP: Fast transmission (DNS, NTP)
- ICMP: Network diagnostics and ping
Port Configuration:
- Source Port: Usually left empty
- Destination Port: Service port
IP Address Configuration:
- Specific IP:
203.0.113.1/32 - Address range:
192.168.1.0/24 - All addresses:
0.0.0.0/0
NEVER allow all IPs (0.0.0.0/0) access to administrative ports like SSH (22) or RDP (3389). Always restrict these to specific IP addresses.
Editing Security Groups
Rules can be modified anytime after creation.
 Figure needed: Security Group editing interface with Add Rule button, existing rules list, and edit/delete options for each rule
Figure needed: Security Group editing interface with Add Rule button, existing rules list, and edit/delete options for each rule
Available Actions:
- Add Rule: Click "Add Rule" and configure
- Edit Rule: Select and update existing rule
- Delete Rule: Click trash icon next to rule
Default Security Groups are read-only and cannot be modified.