Networking Management
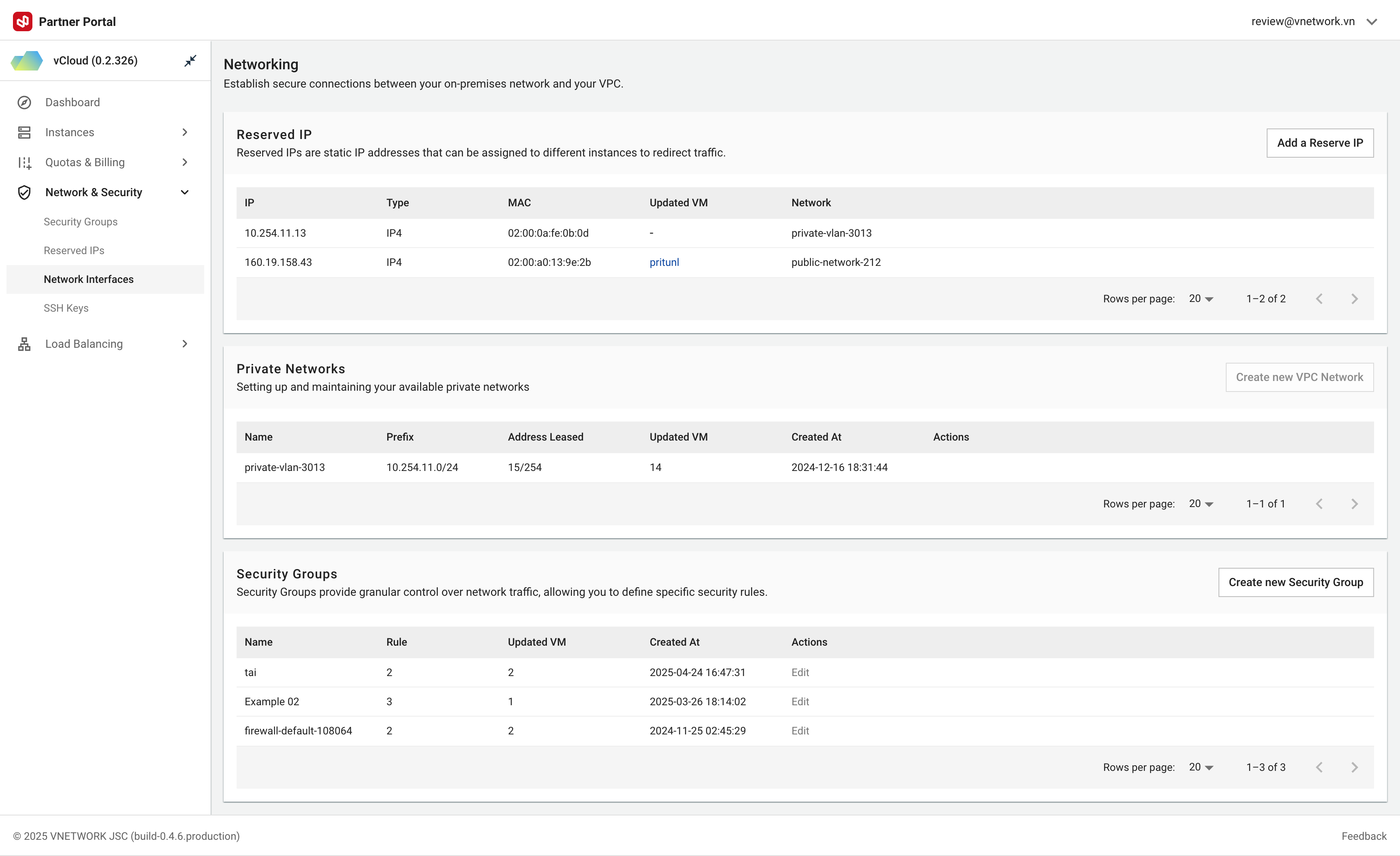 Figure needed: vCloud Networking interface showing main network management dashboard
Figure needed: vCloud Networking interface showing main network management dashboard
The Networking feature provides comprehensive network configuration management for virtual servers, including static IP allocation (Reserved IPs), private network creation (VPC Networks), and security group setup. This enables access control, system segmentation, and cloud infrastructure security.
Accessing Network Management
- Log into vCloud system
- Navigate to Network & Security > Network Interfaces
Core Networking Features
1. VPC Network (Virtual Private Cloud)
VPC Networks create isolated virtual networks for server interconnection without public IPs. All VPC resources are isolated and cannot be directly accessed externally unless specifically configured.
Private Network Information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Internal network name |
| Prefix | CIDR block for internal IP allocation (e.g., 10.254.11.0/24) |
| Address Leased | Used IP addresses / total available |
| Updated VM | Number of VMs attached to this network |
| Created At | Network creation time |
VPC Network Benefits:
- Cost savings: No public IP required for internal servers
- Enhanced security: Network traffic isolation, reduced attack surface
- Flexible connectivity: Easy multi-server connections within same environment
2. Virtual Router
VPC Networks are assigned a random NAT IP to enable internet connectivity for private network servers. Virtual Routers handle packet routing between VPC and external networks.
Virtual Router Features:
- NAT Gateway: Translates internal IPs to public IPs for internet access
- Routing: Directs packets between different networks
- Traffic control: Manages data flow between networks
3. Reserved IP (Static IP Addresses)
Reserved IPs are static IP addresses allocated and dedicated to your account. These IPs can be attached to servers to maintain fixed IP addresses, ensuring service stability even after server restarts.
Reserved IP Information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| IP | Static IP address |
| Type | IP protocol (IPv4) |
| MAC | MAC address associated with IP |
| Attached VM | VM currently using this IP |
| Network | Associated public network name |
Reserved IP Use Cases:
- Web services requiring fixed IP for DNS configuration
- VPN and remote access services
- Database servers needing stable IP for application connections
4. Security Groups
Security Groups act as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic to servers. Create and manage rules to allow or block network traffic based on protocol, port, and IP address.
Security Group Information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Security group name |
| Rule | Number of active rules in group |
| Updated VM | Number of VMs using this security group |
| Created At | Group creation time |
Common Security Rules:
- Allow SSH (TCP port 22) from specific IP addresses only
- Allow HTTP/HTTPS (TCP port 80/443) from all sources
- Block all traffic from untrusted IP addresses
- Allow communication between servers in same private network
Networking Best Practices
Network Design
- Environment segmentation: Create separate VPC Networks for development, staging, and production
- Access control: Use Security Groups with principle of least privilege
- Cost optimization: Use Reserved IPs only when necessary
Network Security
- Minimal access: Open only required ports in Security Groups
- Regular reviews: Periodically audit and update Security Group rules
- VPC isolation: Place servers not requiring public access in private networks
IP Management
- Descriptive naming: Use clear names for Reserved IPs
- Documentation: Record purpose of each static IP
- Efficient usage: Leverage attach/detach capabilities for IP sharing between servers
Detailed Guides
For more information about networking features, refer to these guides:
- Attach Network Interface: Add and configure network interfaces for servers
- Manage Static IP Addresses: Allocate, assign, and manage static IP addresses
- Detach Network Interface: Safely remove network interfaces from servers
- Floating IP: Attach public IP addresses to servers in private networks
For multi-server systems, use VPC Networks for internal communication and Reserved IPs only for services requiring external access to optimize cost and security.